Manage Your First Data
This chapter explains how to create and use your own data structures in Pantarey.
🔗 For in-depth guidance, see Create data structures.
Why data structures matter in Pantarey
Data is the foundation of many business processes. Pantarey lets you build custom data structures and manage records flexibly.
A data structure in Pantarey serves several purposes:
- Validate the information that is entered.
- Automatically generate forms.
- Create data tables for analytics.
This architecture allows processes and data to be combined seamlessly – without external tools or additional systems. Complex data integration becomes unnecessary.
Data in Pantarey
Pantarey manages data in a structured way. A data structure defines which information is stored and how these pieces of information relate to each other.
Examples of data structures:
- Customers.
- Products.
- Inquiries.
- Projects.
- Articles.
- Addresses.
- Invoices.
- Requests.
Each structure consists of fields with different data types (e.g., text, number, date).
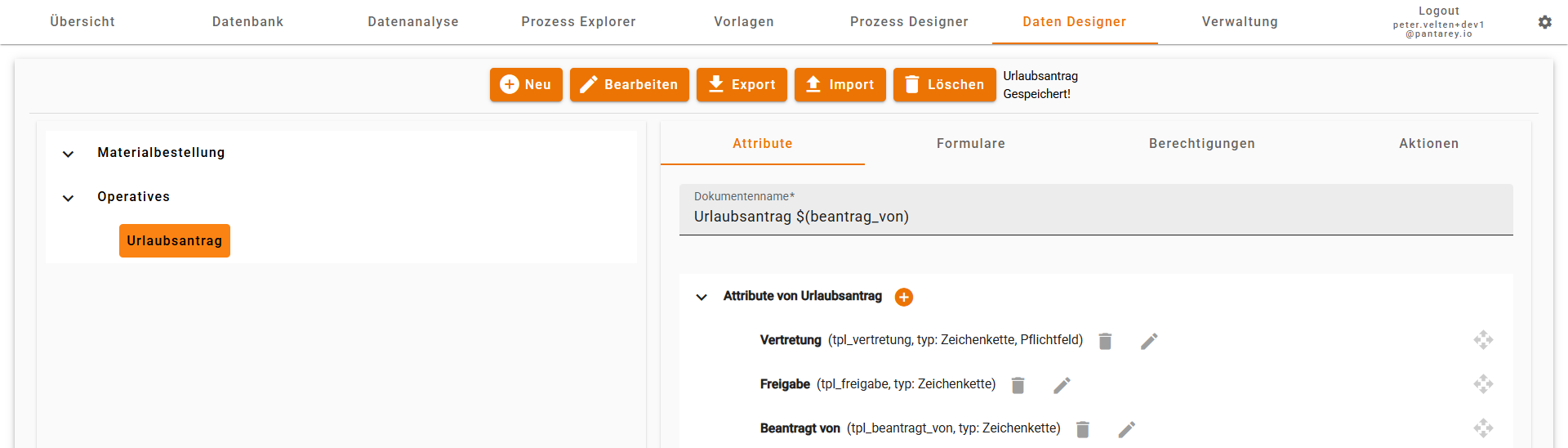
Create a new data structure
New data structures are created in the Data Designer.
Steps:
1. Navigation area
- Select the Data Designer menu item.
2. Create a new data structure
- Click the “New” button.
3. Name, technical name, and description
- Name: choose a clear label.
- Technical name and description: suggestions are generated automatically by AI and can be adjusted if needed.
4. Organize data structures
- Left side: Arrange data structures hierarchically (e.g., “Contact” → “Person” / “Organization”).
- See Inheritance and hierarchies for details.
5. Manage attributes
- Right side: Create and move fields (attributes).
- Add fields such as name, email, or address.
- Changes are saved automatically.
Attributes in detail
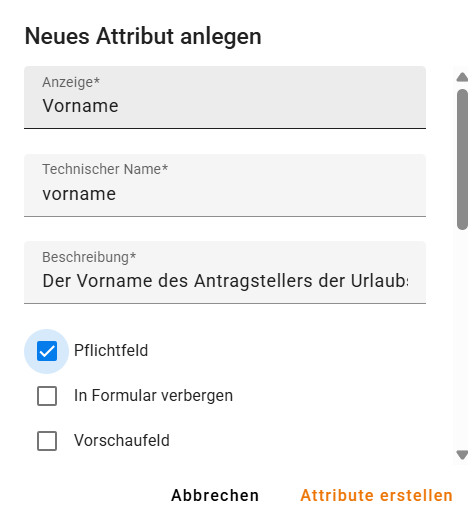
When you add a new attribute, you define information such as:
- Name and technical identifier.
- Data type (text, number, date, reference to other structures).
- Required-field setting.
- Visibility in the form.
- Constraints (e.g., predefined values – ENUM).
Note: The “Reference” data type lets you create relationships between records (e.g., invoice → invoice recipient → address).
Document name
In the header of every structure you can define a document name:
- The document name determines how records are displayed in the overview.
- Example: “Max Sample (max@company.com)”.
Learn more about document names in Preview field and document name.
Advanced features in the Data Designer
Beyond defining attributes, the Data Designer includes other key tabs:
| Tab | Function |
|---|---|
| Forms | Shows the automatically generated forms for data entry. |
| Permissions | Fine-grained access control for records of the structure. |
| Actions | Run bulk data updates and future automations. |
Export and import data structures
- Existing data structures can be exported or imported in JSON schema format.
- The buttons for export and import are located in the navigation bar.
⚠️ Caution: Deleting a data schema permanently removes all related data. Use this feature carefully.
Use data in processes
Pantarey integrates data structures seamlessly into processes:
- Select forms in the start event of a process.
- Display forms automatically for user input.
- Store process data according to the defined structure.
- Use the data in conditions, decisions, and analytics.
Practical examples
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| Vacation request | Capture a request through a generated form. |
| Invoice creation | Select existing customer data within a process. |
| Order handling | Assign products to orders dynamically. |
Summary
Pantarey enables fast, consistent creation of custom data structures. Automatic form generation, flexible use in processes, and centralized data storage support an efficient and scalable way of working.
The next section explains how to expand processes in Pantarey with tasks and decisions.